The article Electricity from raindrops: New generator floats on water first appeared in the online magazine BASIC thinking. With our newsletter UPDATE you can start the day well informed every morning.
Researchers have developed a floating generator that is designed to generate electricity from raindrops. The technology is light, cheap and uses water as an electrode.
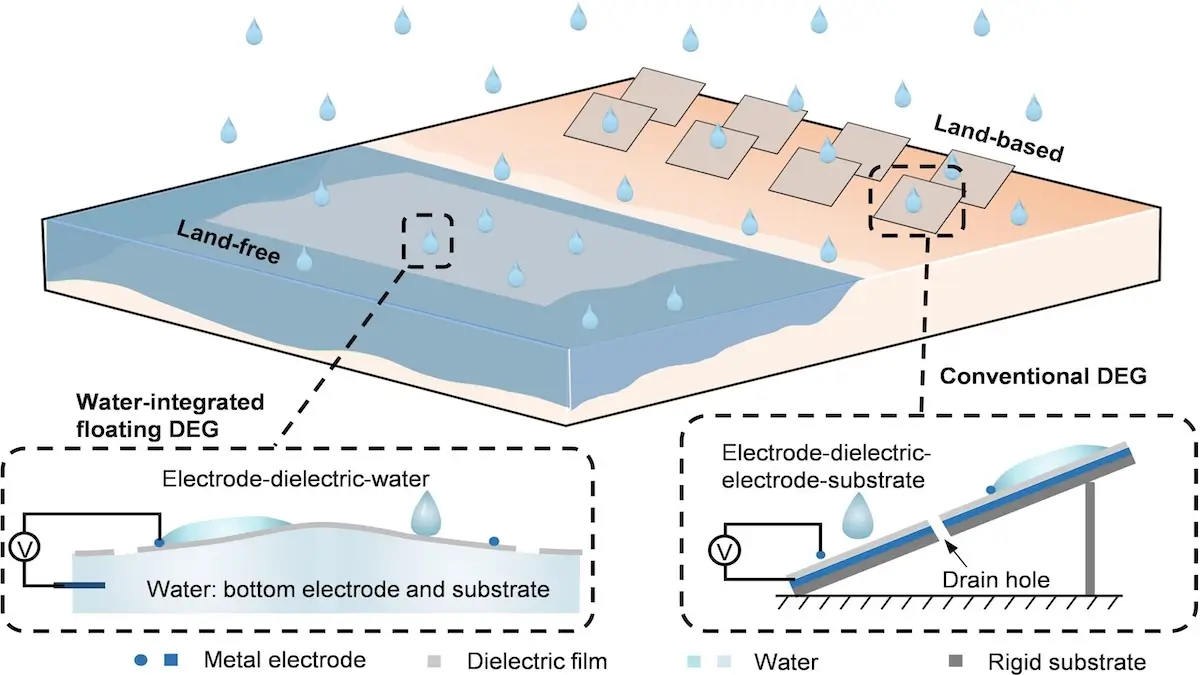
Researchers have a floating one Droplet power generator developed that can generate electricity from raindrops. The new technology uses water itself as an essential part of its structure, acting as both a load-bearing base and a conductive electrode.
In contrast to conventional generators, which are based on rigid and often expensive materials, the new model is lighter, cheaper and more environmentally friendly. At the same time, the structure known as the Water-integrated Droplet Electricity Generator (W-DEG) floats directly on the water. This takes on the role of the substrate and the bottom electrode.
The incompressibility (non-compressibility) and high surface tension of water provide the mechanical stability necessary to absorb the impact of the drop. At the same time, the ions in the water serve as charge carriers and enable it to function as a reliable electrode.
This combination allows the floating generator to produce peak voltages of about 250 volts per drop. The performance is comparable to that of traditional designs based on rigid structures and metal electrodes.
Electricity from raindrops: Significant savings in weight and costs
By integrating water, the material weight could be reduced by around 87 percent and the costs by around 50 percent compared to older models. This makes the W-DEG much easier to transport and use.
The researchers also integrated a 0.3 square meter device that could power 50 LEDs simultaneously. The system was able to charge the built-in capacitors within a few minutes.
The technology is also notable for its durability: tests showed that performance remained stable even under fluctuating temperatures, varying salt concentrations and even in contact with sea or salt water.
The researchers used the surface tension of the water to construct drainage holes that allow water to pass downwards, but not upwards. This prevents water from accumulating on the surface, which would reduce performance.
Applications for land and water
The possible scalability of the generator seems promising. Systems of this type could be used on lakes, reservoirs or in coastal regions. Because they do not require valuable land resources, they complement other renewable energy technologies such as solar and wind power.
The devices could also be used to power environmental monitoring systems, such as sensors that measure water quality or salinity. The idea of nature-integrated design, i.e. using abundant natural materials such as water as functional components, could inspire future approaches in green technology.
However, challenges such as the fluctuating size and speed of real raindrops and ensuring the integrity of large dielectric films under dynamic outdoor conditions still need to be further explored. Only then can the technology be used on a large scale.
Also interesting:
- The most persistent wind energy myths – and what’s true about them
- ChatGPT is listening: This is how you can deactivate background conversations
- Electricity through steps: The future of sustainable energy?
- Vertical wind turbine with AI – for houses in the city
The post Electricity from raindrops: New generator floats on water appeared first on BASIC thinking. Follow us too Google News and Flipboard or subscribe to our newsletter UPDATE.
As a Tech Industry expert, I find the concept of generating electricity from raindrops using a floating generator to be a fascinating development. This innovative approach harnesses the power of nature to create renewable energy, which is crucial for addressing climate change and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
The ability to generate electricity from raindrops opens up new possibilities for sustainable energy production, especially in regions with frequent rainfall. By utilizing a floating generator, this technology can be deployed in bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, or even oceans, maximizing its potential for generating clean energy.
I believe that this technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about renewable energy sources and could play a significant role in transitioning towards a more sustainable future. It will be interesting to see how this technology develops and the impact it has on the energy industry as a whole.
Credits