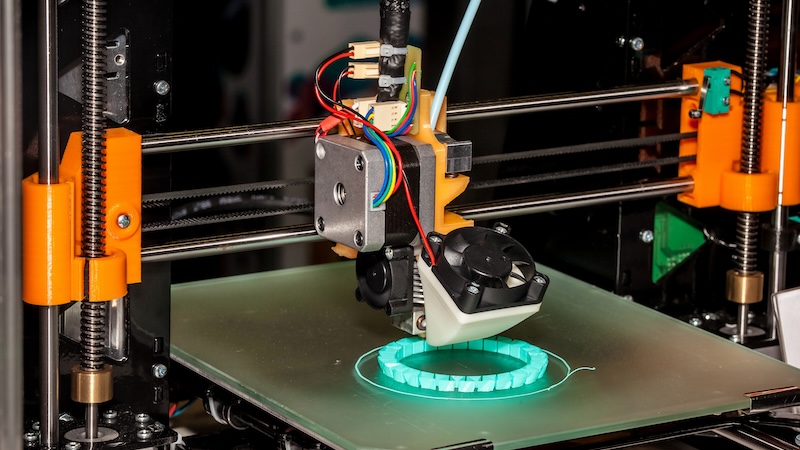
Be it car parts, headphones or prostheses: there is now hardly anything that cannot be printed in three dimensions. Researchers are even working on producing human organs. But how does a 3D printer actually work?
A few years ago there was immense hype surrounding 3D printing. Developers shared fantastic visions they have for the future of technology. Many of the predictions have not yet come true. Nevertheless, 3D printing is now used in numerous areas – for example in research, construction and industry.
3D printing has been around for almost 40 years
The first 3D printer was officially launched by Chuck Hull developed. The inventor filed a patent application for the stereolithography process in 1984 and was awarded the patent. He is also responsible for the development of the STL interface and founded the company 3D Systems in 1986. It brought the world’s first 3D printer onto the market in 1987 under the name SLA-1.
The technology was originally used primarily for so-called prototyping in industry. But further development progressed quickly. Modern 3D printers are now more affordable and user-friendly and are also used privately. Even entire houses can be manufactured using the technology.
How does a 3D printer work?
3D printing is based on building an object layer by layer. Using an additive process, materials such as plastic, metal, resin, ceramics or food are placed on top of each other in many layers until they ultimately form a three-dimensional object.
Before the actual printing begins, however, a digital 3D image must first be created.Model give. Software breaks down the template of the object to be printed into hundreds of thin layers and exports a file in so-called G-code format. This is an older one programming languagewhich provides the printer with precise instructions on where to add the material.
There are different ways to 3D print objects. The following methods are currently most common:
- FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Printing using spools made of plastic fibers
- SLA (Stereolithography): a technology that solidifies photosensitive resin
- PBF (Powder Bed Fusion): a series of powder-based processes that, for example, fuse the particles with powerful lasers
- Material or Binder Jetting: Powdered starting material is glued to selected areas with a binder
The advantages of 3D printing
3D printing can be used to create highly complex objects that cannot be produced using conventional methods. However, one of the main advantages of the technology is speed.
Although the actual printing process can take hours or even days, the turnaround time is usually shorter compared to traditional production methods.
Also interesting:
- Researchers are using AI and 3D printing to revolutionize plant breeding
- Sustainable: This wooden house made from the 3D printer is intended to alleviate the housing shortage
- How does a hybrid car actually work?
- How does air conditioning actually work?
The article How does a 3D printer actually work? by Beatrice Bode first appeared on BASIC thinking. Follow us too Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
As a Tech Industry expert, I can say that a 3D printer works by using a process called additive manufacturing. This means that it builds an object layer by layer, using a digital model as a blueprint. The printer interprets the digital model and deposits material, such as plastic, metal, or resin, in successive layers to create the final 3D object.
The process begins with the digital model being sliced into thin layers by slicing software. The printer then heats up the material to a precise temperature, which allows it to be melted or cured. The material is then deposited onto the build platform in the specific shape of that layer. The platform then moves down slightly, and the process is repeated for each layer until the object is fully formed.
Overall, 3D printing is a versatile and innovative technology that is revolutionizing manufacturing processes across various industries. Its ability to create complex and customized objects quickly and efficiently makes it a valuable tool for designers, engineers, and hobbyists alike.
Credits