The article Lithium of sea water: New membrane for global dismantling first appeared at the online magazine Basic Thinking. You can start the day well every morning via our newsletter update.
Researchers have found a way to filter lithium from sea water. A new membrane should enable global filtering and ensure enough material for future energy storage.
Lithium is considered the key element of modern technologies. The light metal is used in batteries for electric vehicles, smartphones or laptops. But the increasing demand and geopolitical challenges are a problem.
A new development of the Argonne National Laboratory In cooperation with the University of Chicago, however, promises. A new membrane should be able to filter lithium from sea water and enable worldwide breakdown.
The technology could not only reduce the dependency on traditional deposits, but also open up new sources. Because in the sea water there are almost inexhaustible lithium occurrence that make up over two thirds of the well -known reserves.
Lithium made of sea water: high -tech membrane on tone -based
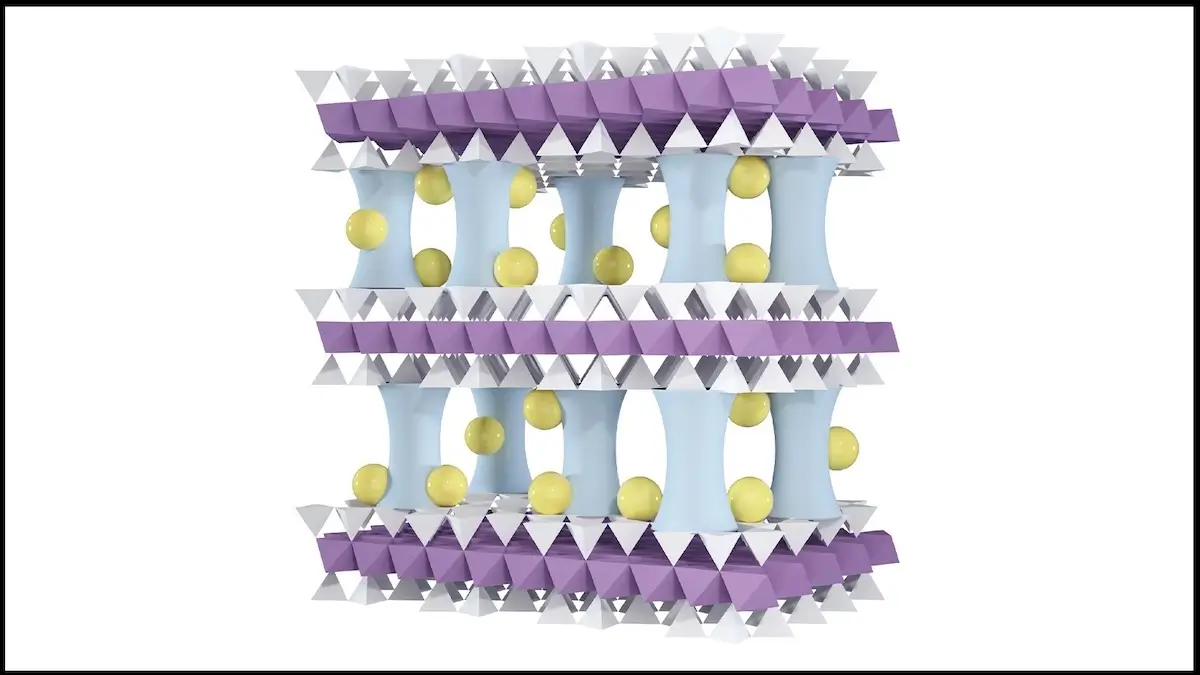
The basis of the new separation technology forms Vermiculitean inexpensive tone that is characterized by its high ion replacement capacity. However, the material quickly dissolves into water. The researchers met this problem by inserting aluminum oxide pillars between the ultra-thin clay layers.
These stabilize the structure and neutralize the electrical surface load, which enables targeted modification. The membrane is generally charged positively by further treatment with sodium ions. Since lithium and magnesium ions are both positive, but magnesium has a double positive load, it is rejected more.
Lithium, on the other hand, can be filtered out efficiently. In addition, a finely adjusted pore size also allows a separation from other elements such as sodium and potassium. The materials used are not only cheap (Vermiculit costs about $ 350 per ton), but also durable.
The membrane could be used for over five months in experiments. If the technology is established on the industrial scale, deep water sources could even be economically developed. There, the lithium concentration is around 1000 times higher than in the sea.
Lithium reduction: opportunities and challenges
At the same time, the procedure also opens up perspectives for the recovery of further critical raw materials such as nickel or rarer earth. Water treatment should also be possible. The researchers see this a basic building block for a sustainable resource policy.
The new membrane technology could be a step towards sustainable lithium extraction. It promises an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional, often resource -intensive degradation methods. But until industrial use, many questions still have to be clarified:
Can the membrane production be economically implemented on a large scale? Or: How robust is the material in constant use under real conditions? Nevertheless, the development shows how scientific innovation can help to solve global resource problems.
Also interesting:
- What influence have solar parks on the environment and ecosystems?
- Chatgpt: Delete all chats at once – that’s how it works
- Why e-cars on cargo ships are no greater danger
- Element: Everything you need to know about the WhatsApp alternative
The contribution lithium of sea water: New membrane for worldwide dismantling first appeared on Basic Thinking. Follow us too Google News and Flipboard Or subscribe to our update newsletter.
As a tech industry expert, I am intrigued by the potential of using lithium from seawater as a new source for lithium production. The development of a new membrane for worldwide dismantling could revolutionize the lithium industry and address the growing demand for this crucial element in various technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
This innovation has the potential to significantly reduce our reliance on traditional lithium sources, such as lithium mines, which can have negative environmental and social impacts. By extracting lithium from seawater, we can tap into a virtually limitless supply of this valuable resource while minimizing the environmental footprint of lithium production.
However, it is important to consider the challenges and potential drawbacks of this approach, such as the energy and cost requirements of extracting lithium from seawater on a large scale. Additionally, the development and deployment of the new membrane technology will require significant investment and infrastructure to make it commercially viable.
Overall, I believe that the use of lithium from seawater has the potential to be a game-changer for the tech industry and could help ensure a sustainable and secure supply of lithium for future generations. It will be exciting to see how this technology develops and how it shapes the future of the lithium industry.
Credits