The article With tea: Researchers want to breathe new life into electric car batteries first appeared in the online magazine BASIC thinking. With our newsletter UPDATE you can start the day well informed every morning.
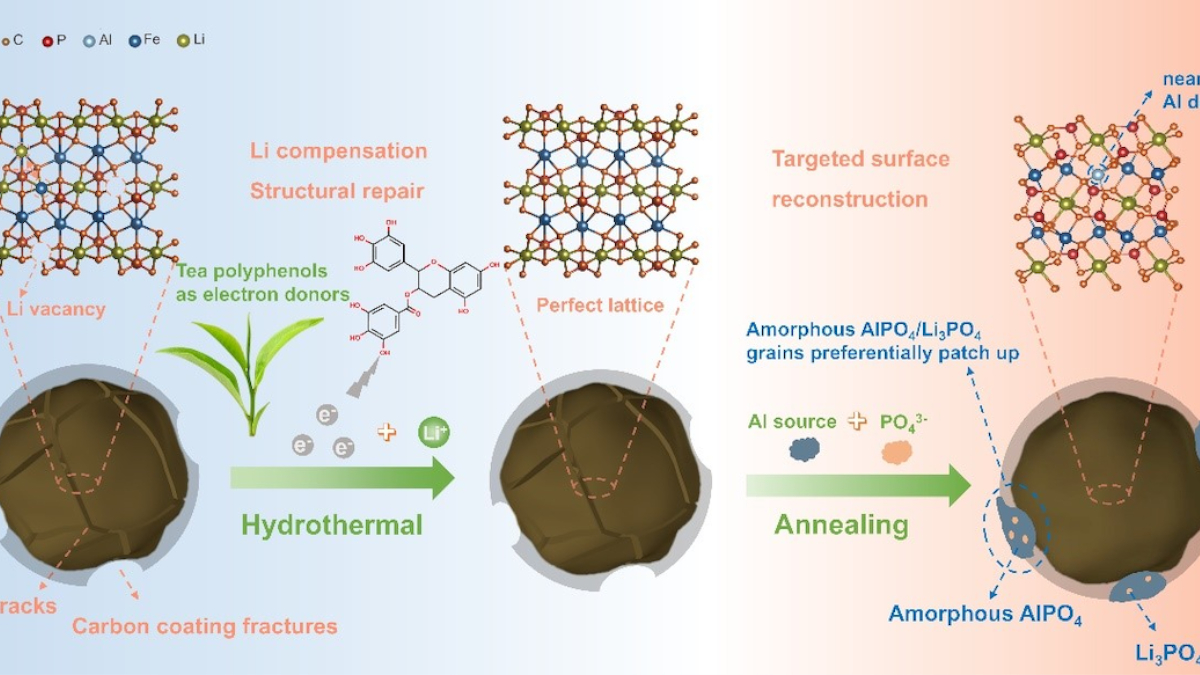
Researchers in China have discovered that active ingredients from tea leaves can regenerate used lithium-ion batteries. Their method repairs crystalline defects and creates pathways that could make used batteries usable again.
Whether in smartphones, electric cars or in large-scale stationary storage systems for solar and wind energy – lithium-ion batteries are almost ubiquitous today. Because they can store a lot of energy in a small space and can also be recharged multiple times.
If the batteries get old, they can also be recycled. But recycling lithium-ion batteries is complex because they consist of many closely related materials.
In addition, common processes are often very energy-intensive and expensive, so the extraction of new raw materials can have economic advantages over recycling. In addition, important materials such as lithium or graphite are often lost in the recycling process, while recovery usually focuses on valuable metals such as nickel or cobalt.
Researchers from China want to avoid these negative aspects of recycling lithium-ion batteries in the future. They have found a way to regenerate them with the help of tea instead.
Can tea breathe new life into old electric car batteries?
In the coming years, the number of lithium-ion batteries used and recycled will increase significantly, among other things as a result of the expansion of electromobility. According to one Forecast from Fraunhofer ISI Around 520 kilotons of lithium-ion batteries are expected to be recycled within the EU by 2030 alone. For comparison: In 2024 it was still around 120 kilotons.
This process could be made significantly cheaper through the discovery of Chinese scientists. The researchers at the Hefei Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences were able to develop a regeneration process for lithium-ion batteries using naturally derived tea polyphenols.
They are doing their work together with scientists from Tsinghua University and Suzhou University of Technology in the scientific journal Advanced Materials published. Here they describe their process, which offers a cost-effective, energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional recycling.
This is how the regeneration of lithium-ion batteries works
The scientists focused their work on the regeneration of degraded cathode materials. The conventional recycling process is often unprofitable for them.
Natural substances from tea were used, which can repair defects in the material of the batteries and thus make them functional again. The tea polyphenols used are used as electron donors.
The composition and structure of the material could be completely restored. This created new pathways for ions, which significantly improved the performance and stability of the battery.
In addition, the researchers used aluminum during the regeneration process, which attaches itself to damaged areas and forms a protective layer there. In this way, old cathodes could be restored and their lifespan extended.
Also interesting:
- Zinc-air battery: New catalyst increases service life and performance
- LFP battery: Renault relies on a new cheap battery
- Prototype: Researchers develop the first hydride-ion battery
- IBIS battery: Stellantis presents new AC battery
The post With tea: Researchers want to breathe new life into electric car batteries appeared first on BASIC thinking. Follow us too Google News and Flipboard or subscribe to our newsletter UPDATE.
As a tech industry expert, I think the idea of using tea to improve electric car batteries is innovative and exciting. Tea contains compounds that have been found to be effective in enhancing the performance and longevity of batteries. By leveraging the unique properties of tea, researchers have the potential to develop more efficient and sustainable battery technology for electric vehicles.
This approach not only has the potential to improve the overall performance of electric car batteries but also to reduce their environmental impact. By using natural and renewable materials like tea, we can move towards more sustainable energy storage solutions that minimize the use of harmful chemicals and reduce the carbon footprint of electric vehicles.
Overall, I believe that this research holds great promise for the future of electric car batteries and has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our vehicles. I look forward to seeing how this technology develops and how it can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation industry.
Credits